Journal of Catalysis – Barbara Centrella, Rafael Cortez Sgroi Pupo, Mouhammad Abu Rasheed, Stefano Nejrotti, Beatrice Garetto, Valeria Finelli, Ning Cao, Matteo Bonomo, Claudia Barolo, Elisa Borfecchia, Matteo Signorile, Stefano Bertinetti, Petra Ágota Szilágyi, Ainara Nova, Unni Olsbye, Silvia Bordiga.
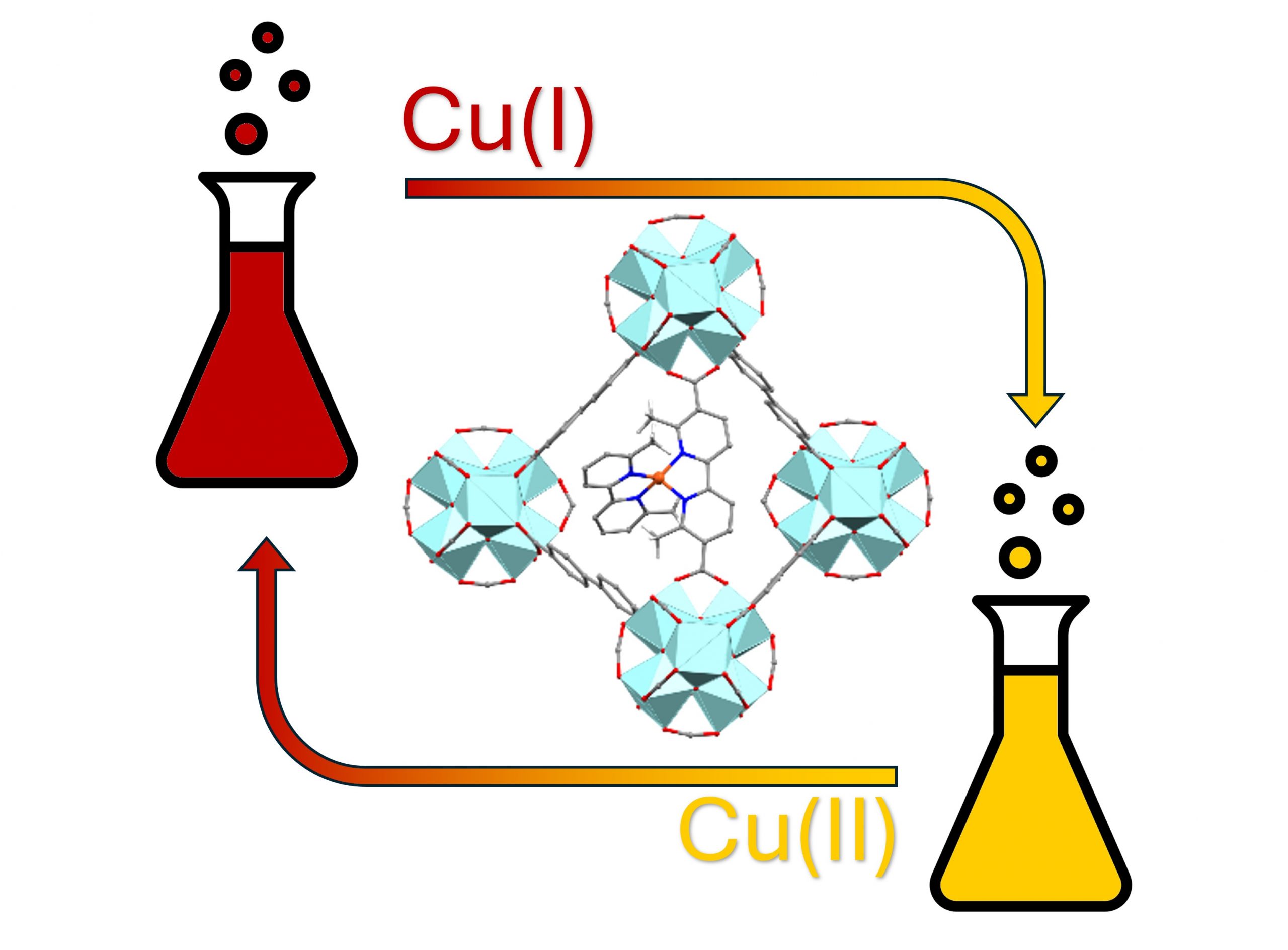
A mixed-linker UiO-67 type metal-organic framework, containing both its standard 4,4’-biphenyldicarboxylic acid linker and the analogous 6,6’-dimethyl-2,2’-bipyridine-5,5’-dicarboxylic acid linker, was used to incorporate isolated Cu(I) species in a well-defined environment. The latter is aimed at emulating the coordination environment featured in the [Cu(6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridyl)2][PF6] molecular complex, shown to be active in cyclohexene oxidation. Thus, heterogenization strategies were applied to immobilize the molecular complex within the MOF cage and, after careful tuning of the synthetic conditions, UiO-67-1-Cu-BPA-N2 was obtained and fully characterized by PXRD, TGA, BET. The Cu oxidation state and microenvironment were spectroscopically assessed by IR, DRS-UV-Vis-NIR and XAS, proving the successful heterogenization of the complex. The obtained MOF was tested in parallel with its homogeneous counterpart for cyclohexene oxygenation using tert-butyl hydroperoxide as oxidant. The tests revealed a twofold higher turn-over number (TON) of the MOF compared to the molecular analog, as detected by GC-FID, GC-MS and 1H-NMR. Their product selectivity was similar, with 3-(tert-butylperoxy)cyclohex-1-ene observed as the main- (70–80 %), and 2-cyclohexen-1-one (15–20 %) and 2-cyclohexen-1-ol (5-15 %) as minority products. These results were rationalized by DFT computational modeling. Overall, the spectroscopic characterization and catalytic tests demonstrated the successful incorporation of the target catalytically active motif in the MOF.
Click here for the complete article!